What Is Hybrid Cloud Storage? What are the Benefits?
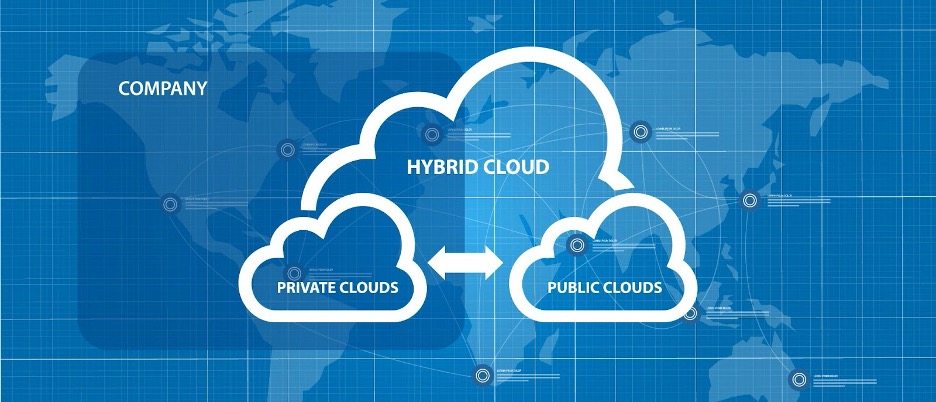
Curious about hybrid cloud storage? We explain how a hybrid cloud environment can help you build a cost-effective, flexible, and efficient operating model.
What is hybrid cloud storage?
Hybrid cloud storage refers to a mixed storage environment using both local and off-site resources. This modern solution includes on-premises, private cloud services, and the public cloud. The combination of mixed storage provides businesses with the ability to adapt to changing business needs.
What are the Different Types of Cloud Environments?
Not all cloud services are made the same, and the differences can have a significant impact on businesses or other organizations using those resources, whether that is due to security issues or performance, or any number of factors.
Generally, there are three types of cloud environments:
- Public Cloud: The environment that most consumers (and many businesses) are familiar with. Public cloud infrastructure is built on servers, networks, and storage using shared resources delivered by a third-party provider. This doesn’t mean that user information overlaps from one organization to the next. Instead, it means your data and applications run on a resources shared with other users (called tenants).
Generally speaking, the benefits and the limitations of public clouds stem from the sharing of servers. It’s typically faster, and less expensive to get started building applications on Public cloud services like storage or cloud computing. Public cloud providers deliver infrastructure in a global footprint with high reliability and scalability. The fact that a server can host multiple tenants can lead to performance (such as noisy neighbor) concerns, and can rub against certain regulations in some industries and regions, however.
- Private Cloud: The opposite of public cloud, private cloud infrastructure allows for a single organization to use server resources without sharing those resources. This can be accomplished in multiple ways, typically either through on-premises local cloud installations or single-tenant cloud servers hosted by providers.
Private cloud environments can be much more flexible to the needs of the organization using them, and this includes additional layers of control and customization due to their complete ownership of the cloud resources. Private clouds can also help boost cybersecurity by reducing attack surfaces that exist on shared servers.Following these benefits, there are some drawbacks. Private cloud is expensive, much more so than public cloud. Private cloud often requires more work to build, manage, and maintain the underlying resources, especially if deployed on-prem, which can slow down new projects and limit organization’s ability to scale on-demand.
- Hybrid Cloud: To get the most from the benefits of both public and private infrastructure, providers offer cloud solutions that bring together the performance and privacy of a private cloud with the accessibility, elasticity, and reduced cost of public cloud
One of the biggest advantages of hybrid cloud infrastructure is that it provides ways to run applications where they deliver the most value to customers. For example, by combining private and public aspects of your cloud to leverage higher performance (and higher costs) versus maintained and less expensive public cloud services when performance isn’t needed.
Hybrid cloud storage architecture, therefore, focuses on prioritizing workloads and storage around optimized resource usage.
Hybrid Cloud Storage Explained
One of the more important features of any cloud system is storage. Hybrid cloud storage is the practice of managing cloud storage across both public and private cloud environments to best suit the needs for the application. More specifically, most organizations will see cloud storage as a way to use combinations of public, private off-site and on-prem storage as needed to deliver the right combination of cost, scale, performance, and security to support their business
Primarily, hybrid cloud environments involve both public and private cloud , bringing together functionality between the two using APIs or other processes. These cloud environments are still different and autonomous from one another. The connectors and applications connecting them, however, do so in a way to render that distinction between one environment invisible to users and workflows so that your IT team or cloud partner can plan a streamlined hybrid cloud strategy.
The biggest benefit of cloud systems is that you can store any kind of data in a hybrid environment rather than on any public or private cloud. Through technologies like cloud filesystems and shared databases, it’s possible to manage a variety of storage media and platforms at the same time while maintaining a uniform access interface for your people and apps.
What are Some of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud Storage?
Organizations turn to hybrid cloud infrastructure so they have greater flexibility to run workloads wherever they can deliver the best performance, with the greatest security and control, at the lowest cost.
The characteristics of this approach include:
- Homogenous Storage: Properly configured, a hybrid storage solution is homogeneous to users. That is, a regular user, like an employee, should not see the split between local and off-site data storage. It will all appear as a single, contiguous file system.
- On-Demand Performance: If you need faster access or increased throughput for data transfers or data reads for specific files or data sets, then hybrid cloud storage can provide that performance for key files and databases. Hybrid cloud environments allow for strategic resource allocation between public and private resources. Through a practice called “cloud bursting”, your hybrid system can shift resources to available public cloud servers if their private resources are at 100 percent.
- Effective Disaster Recovery Planning: Archiving and data backups are key aspects of disaster recovery and business resiliency. A hybrid solution provides a way to keep important data in on-prem services while automating backups to public (and secure) cloud servers. This can improve RTO and RPO efforts.
- Portable Workflows and Workloads: If you’re using compute-intensive workloads on your cloud infrastructure for things like AI or analytics, then a cloud can support flexibility in that regard. This means prioritizing workloads in dedicated on-prem resources and leaving the rest in public infrastructures.
What Are Some Challenges of Hybrid Cloud Environments?
While hybrid cloud environments provide quite a bit in terms of optimization and cost reduction, they are not without their own challenges.
Some of these challenges include:
- Security: One of the major selling points of private cloud systems is security and privacy. When introducing public resources on shared servers, you could possibly open yourself to cybersecurity vulnerabilities or non-compliance. It’s important to have all security measures in place, with a clear idea of the risk and governance practices that can help maintain your hybrid cloud storage environment.
- Complexity: Connecting files across multiple servers is one thing. Implementing complex workflows and workloads across servers automatically is another. Integrating multiple cloud environments takes a skilled provider or experienced IT team to implement and maintain.
- Network Design: Maintaining files in a hybrid storage solution isn’t a challenge on its own. Using that stored data to do work over multiple applications across multiple clouds calls for a deep understanding of the underlying network protocols, requirements, and hardware limitations.
Hybrid Cloud vs Multi Cloud: Are They the Same?
In short, no.
A hybrid cloud environment is a collection of different cloud deployment modes (public or private) interconnected through software and hardware. As previously discussed in this article, this means that your system is simply leveraging different configurations of cloud infrastructure.
Multi Cloud, on the other hand, is an amalgamation of different cloud services in a single environment. For example, a multi cloud environment might use different SaaS applications or PaaS operating system instances across both Microsoft Azure and Amazon AWS cloud platforms under a singular multi cloud environment.
Generally speaking, a hybrid cloud is technically a multi cloud, but a multi cloud is not always a hybrid cloud. A collection of cloud features and apps could technically fall under the definition of a multi cloud, but if they are all hosted on public cloud servers then it would not be hybrid cloud storage. Refer to our learning center resource for more on the difference between hybrid cloud and multi cloud.
Hybrid Cloud Storage for High-Performance Computing with WEKA
One of the more important tools you can have to maximize your cloud environment is a data platform that supports contiguous storage and high-performance computing (HPC) across your system.
The WEKA data platform for hybrid cloud provides the infrastructure that your organization needs to optimize HPC across a cloud environment. With WEKA, you can drive cloud workloads with amazingly high performance for some of the most demanding computing tasks you can think of, including complex analytics for life science and AI applications.
Importantly, the same WEKA software supports customers on-premises solutions and cloud infrastructures, enabling easy data portability and seamless migrations between on-premises and cloud environments. The approach is foundational to enabling customers hybrid cloud strategies
This approach includes on-demand access to resources through cloud bursting, rapid spin-up for new compute instances and S3 tiering for unlimited scaling capacity.
Additional Helpful Resources
Hybrid Cloud Strategy
FSx for Lustre
BeeGFS Parallel File System Explained
Learn About HPC Storage, HPC Storage Architecture and Use Cases
Isilon vs. Flashblade vs. WEKA
NAS vs. SAN vs. DAS
Network File System (NFS) and AI Workloads
Block Storage vs. Object Storage
Modern Data Architecture
WEKA Unleashes Its Blazingly Fast S3 Protocol Front End
What is Cloud Storage?
Cloud Bursting